- Email: info@clearinfosec.com
- 1800 760 5656

In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, even tech giants like Microsoft are not impervious to the sophisticated tactics employed by threat actors. The recent cybersecurity incident that befell Microsoft marked not just a breach but a watershed moment in the company’s history. This extensive blog aims to unravel the intricacies of this incident, from its initial discovery to the far-reaching consequences, the lessons it imparts to the tech industry, a closer examination of the operational infrastructure utilized by the threat actors, and crucial recommendations to fortify organizations against such attacks.
In the latter part of November 2023, cybersecurity researchers at Proofpoint unearthed a campaign of unparalleled sophistication. This malicious endeavor seamlessly blended credential phishing with the ominous cloud account takeover (ATO) technique, creating a potent threat that was not only persistent but highly adaptive. What set this campaign apart was its ability to entice users with personalized phishing lures cunningly embedded within shared documents.
These seemingly innocuous documents harbored a dangerous secret – links adorned with seemingly benign texts like “View Document.” Once users interacted with these links, they found themselves redirected to malicious phishing webpages, ensnared in a trap set by meticulous threat actors.
The fallout from this cyber onslaught was far-reaching, impacting organizations on a global scale. Unlike many cyber incidents that target a specific sector or demographic, this campaign displayed a lack of discrimination in its selection of targets. From Sales Directors to executive positions such as “Vice President, Operations,” the threat actors cast a wide net, aiming to compromise accounts with varying levels of access.
This diverse impact raised questions about the strategic intent behind the attack. The choice of targets suggested a meticulous approach, aiming to infiltrate organizations at various levels and potentially gain access to a treasure trove of sensitive information and resources.
Understanding the anatomy of this cyber attack is essential to comprehend its severity. Threat analysts, in their pursuit of unraveling the incident, identified specific Indicators of Compromise (IOCs). A distinctive Linux user-agent emerged as a key element, providing insight into unauthorized access to various Microsoft365 apps.
The aftermath of successful initial access unveiled a sequence of unauthorized post-compromise activities, each more insidious than the last. From manipulations of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) methods to data exfiltration, internal and external phishing, financial fraud attempts, and the creation of mailbox rules, the attackers left no stone unturned.
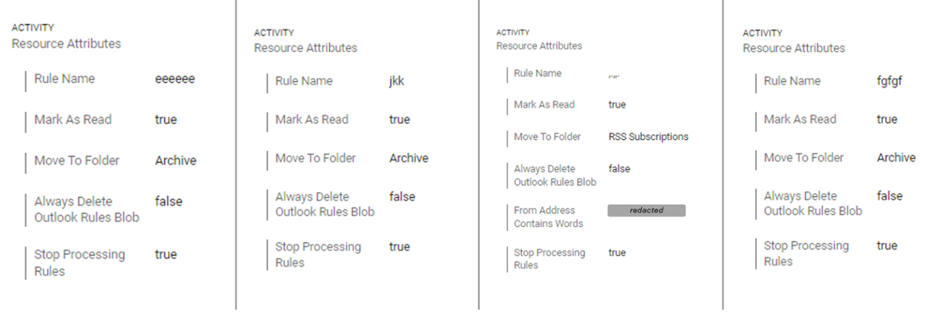
figure 1: Post-account takeover example, attackers creating obfuscation mailbox rules.
Their techniques revealed a profound understanding of both technological vulnerabilities and human psychology. The use of deceptive links embedded in documents showcased a keen awareness of human behavior. Links with seemingly innocuous texts like “View Document” played on users’ natural inclination to trust familiar prompts, ultimately leading them into the clutches of the threat actors.
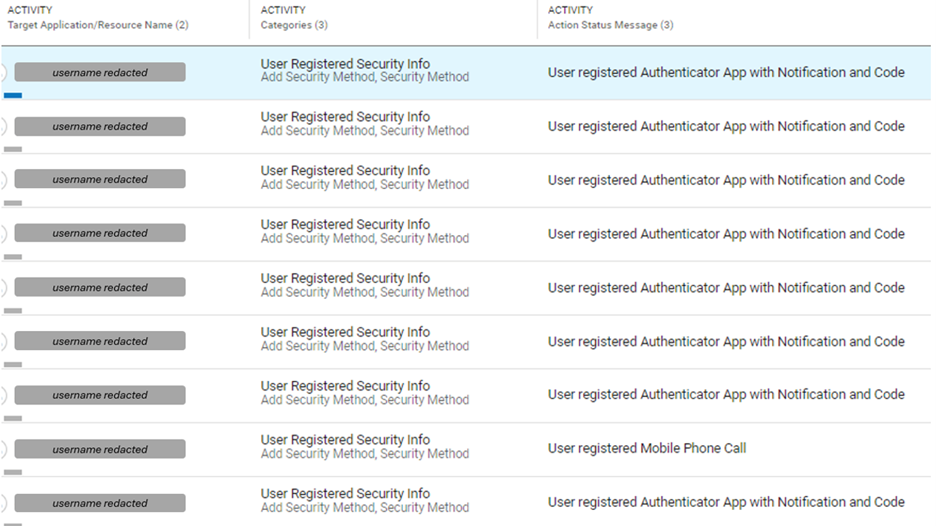
figure 2: Compromised cloud tenant Example: attackers manipulating MFA.
The primary objectives of the cyber onslaught were financial fraud and data theft. The potential manipulation of the Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) system heightened the severity, granting threat actors the power to alter recovery phone numbers or install app authenticators, thereby extending their control over compromised accounts.
The incident not only shed light on the vulnerabilities within Microsoft’s security infrastructure but also brought forth industry-wide concerns. Amit Yoran, CEO of Tenable, had previously voiced his concerns about Microsoft’s poor cybersecurity measures, describing their track record as “even worse than you think.” Yoran highlighted a recurring pattern of negligence, leading to multiple data breaches, extending to espionage by the Chinese government on the US government and its citizens.
This critique from a cybersecurity industry leader underscored the need for a robust and proactive approach to cybersecurity within tech companies. Microsoft, being a behemoth in the industry, faced not just scrutiny but also the responsibility to set a high standard for security practices.
The incident involving Microsoft served as a microcosm of broader security challenges within the tech industry. Security breaches, once considered anomalies, now cast a long shadow over the digital landscape. The response from the U.S. government indicated not only the severity of the incident but also the collective urgency to address the escalating menace of cyber threats.
The incident prompted a broader reflection on the need for transparency and the disclosure of significant data breaches within the tech industry. The prevalence of security breaches, not just in Microsoft but across various tech companies, underscored the imperative for accountability and proactive measures to safeguard sensitive information.
In the intricate web of a cybersecurity incident, the operational infrastructure employed by threat actors often serves as a critical piece of the puzzle. Forensic analysis of the recent attack on Microsoft has unraveled a nuanced understanding of the attackers’ operational tactics, shedding light on the sophisticated maneuvers executed to conceal their tracks and maximize the impact of their malicious activities.
The forensic scrutiny of the attack revealed a multifaceted operational infrastructure utilized by the threat actors. Proxies, data hosting services, and hijacked domains emerged as the key components constituting the attackers’ toolkit. These elements played a pivotal role in orchestrating the attack while simultaneously presenting challenges for defenders seeking to thwart malicious activities.
One notable aspect of the attackers’ strategy was the shrewd use of proxy services. These services served a dual purpose – not only did they facilitate unauthorized activities, but they also played a crucial role in aligning the apparent geographical origin of these activities with that of the targeted victims. This tactical maneuver served as a means to evade geo-fencing policies, confounding defenders attempting to trace the source of the attack.
Furthermore, the threat actors demonstrated a high level of sophistication by frequently alternating proxy services. This dynamic approach not only masked their true location but also posed an additional challenge for defenders attempting to block malicious activity. The strategic use of proxy services showcased the threat actors’ commitment to operational secrecy and adaptability in the face of potential countermeasures.
Beyond the realm of proxy services, the analysis unearthed the utilization of certain local fixed-line ISPs by the threat actors. This choice potentially exposed their geographical locations, providing a glimpse into the origins of the attack. Notable among these non-proxy sources were the Russia-based ‘Selena Telecom LLC’ and Nigerian providers ‘Airtel Networks Limited’ and ‘MTN Nigeria Communication Limited.’
This revelation adds an intriguing layer to the investigation, raising questions about the geographical distribution of the threat actors and potential insights into their affiliations. The choice of specific ISPs indicates a deliberate strategy, offering a glimpse into the geographical landscape that these threat actors may inhabit.
While the forensic analysis has provided valuable insights into the attackers’ operational infrastructure, the attribution of this campaign remains elusive. At present, Proofpoint has refrained from attributing the campaign to any known threat actor. However, a noteworthy observation emerges – the possibility of Russian and Nigerian involvement, drawing parallels to previous cloud attacks.
This conjecture adds complexity to the incident, hinting at potential similarities in tactics, techniques, and procedures employed by threat actors from these regions. The historical context of cloud attacks involving Russian and Nigerian actors becomes a relevant point of consideration, urging a nuanced exploration into the motivations and affiliations of the threat actors involved.
In the wake of this sophisticated cyber attack, organizations must proactively strengthen their cyber defense mechanisms. The following recommendations provide a roadmap for fortifying your organization against similar threats:
In the intricate landscape of a cybersecurity incident, the operational infrastructure employed by threat actors serves as a critical thread in unraveling the entire tapestry. The use of proxies, data hosting services, and local fixed-line ISPs unveils a strategic dance between concealment and exposure, where threat actors deploy sophisticated tactics to navigate the digital realm.
As the investigation continues, the revelation of the attackers’ operational infrastructure offers a deeper understanding of their modus operandi. The geographical deceptions through proxies, exposure through local ISPs, and the potential Russian and Nigerian parallels underscore the need for a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, this analysis not only aids in understanding the specifics of the Microsoft attack but also contributes to the broader discourse on cybersecurity strategies. The challenges posed by operational infrastructure demand continual vigilance, adaptability, and collaboration within the cybersecurity community to fortify defenses against the relentless ingenuity of threat actors.
12, F., & The Proofpoint Cloud Security Response Team. (2024, February 12). Community alert: Ongoing malicious campaign impacting Azure Cloud Environments: Proofpoint us. Proofpoint. https://www.proofpoint.com/us/blog/cloud-security/community-alert-ongoing-malicious-campaign-impacting-azure-cloud-environments
Chowdhary, K. (2024, February 21). Microsoft Azure hit with the largest data breach in its history; hundreds of executive accounts compromised. The Tech Report. https://techreport.com/news/microsoft-azure-hit-with-the-largest-data-breach-in-its-history-hundreds-of-executive-accounts-compromised/
Copyright © 2026 Clear Infosec. All Rights Reserved.