- Email: info@clearinfosec.com
- 1800 760 5656

In today’s digital world, protecting sensitive information and data is of utmost importance. That’s why many organizations turn to international standards like ISO 27001 to establish robust information security management systems (ISMS). Implementing ISO 27001 can provide a framework for identifying risks, implementing controls, and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the process of implementing ISO 27001, covering everything you need to know to achieve certification. From assembling an implementation team to maintaining continuous compliance, we will explore each phase of the certification process. So, let’s dive in and discover how you can effectively implement ISO 27001 and safeguard your organization’s information assets.
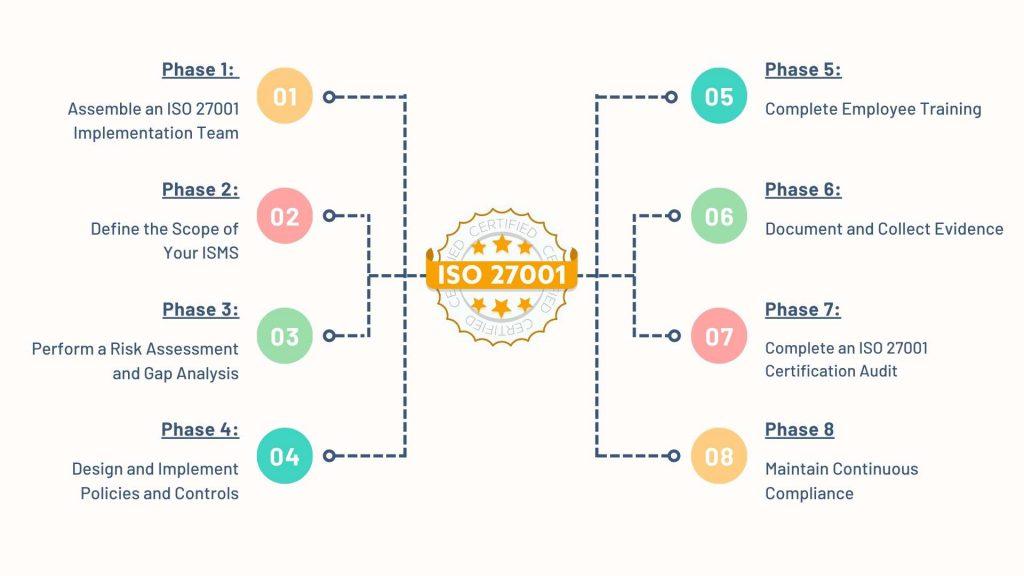
Implementing ISO 27001 requires collaboration and coordination across various departments within your organization. The first step is to assemble an ISO 27001 implementation team. This team will be responsible for driving the implementation process and ensuring that all necessary steps are taken to achieve certification.
The implementation team should consist of individuals with diverse expertise and knowledge in information security, risk management, and organizational processes. It is crucial to appoint a project leader who will oversee the implementation project and work closely with other team members to create a project plan.
The project plan should outline the objectives, timeline, and budget for the implementation project. It should also address the management support and resources required to successfully implement ISO 27001. By assembling a dedicated team and creating a well-defined project plan, you set the stage for a successful implementation journey.
Before diving into the implementation process, it is essential to define the scope of your Information Security Management System (ISMS). The scope determines the boundaries and extent of your ISMS implementation and certification.
To define the scope, you need to identify the assets, processes, and departments within your organization that will be included in the ISMS. This involves understanding the information assets that need protection, such as customer data, intellectual property, and sensitive business information.
The scope can be broad, encompassing the entire organization, or specific to certain departments or systems. It is crucial to align the scope with your organization’s goals, objectives, and the expectations of your customers and stakeholders. By clearly defining the scope of your ISMS, you can focus your efforts and resources on protecting the most critical information assets.
One of the fundamental requirements of ISO 27001 is conducting a risk assessment. A risk assessment helps identify potential threats and vulnerabilities to your organization’s information assets. It allows you to prioritize risks and implement appropriate controls to mitigate them effectively.
To perform a risk assessment, you need to identify the assets, threats, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts associated with your information assets. This can be done through interviews, document reviews, and technical assessments. The goal is to understand the likelihood and potential impact of various risks to your organization.
Once the risks are identified, you can conduct a gap analysis to compare your existing security controls with the requirements of ISO 27001. The gap analysis helps you identify areas where your organization falls short in meeting the standard’s requirements. It provides valuable insights into the necessary improvements and actions needed to achieve compliance.
Based on the results of the risk assessment and gap analysis, you can design and implement policies and controls to address the identified risks. Policies serve as high-level guidelines and principles that define how your organization approaches information security.
The policies should cover various aspects of information security, such as access control, incident response, asset management, and business continuity. They should align with the requirements of ISO 27001 and reflect your organization’s specific needs and risk appetite.
Controls, on the other hand, are specific measures and mechanisms implemented to mitigate risks. These controls can include technical controls, such as firewalls and encryption, as well as procedural controls, such as access control procedures and training programs.
It is essential to ensure that the implemented controls are documented, communicated to employees, and regularly reviewed and updated. By designing and implementing robust policies and controls, you establish a strong foundation for your ISMS and enhance the security of your information assets.
One of the critical success factors for ISO 27001 implementation is employee awareness and training. All employees within your organization should be trained on information security best practices and their roles and responsibilities in maintaining the security of information assets.
Training programs should cover topics such as data protection, password security, incident reporting, and handling sensitive information. By providing comprehensive training, you empower your employees to become active participants in your organization’s information security efforts.
Training can be conducted through various methods, including online courses, workshops, and awareness campaigns. Regular refresher training should also be provided to ensure that employees stay up-to-date with the latest security practices and policies.
Documenting your ISO 27001 implementation is crucial for demonstrating compliance and preparing for the certification audit. You need to maintain detailed records of your policies, procedures, risk assessments, training programs, and other relevant documents.
Collecting evidence involves gathering documentation and artifacts that prove the implementation of your ISMS. This can include records of training sessions, audit reports, incident response logs, and evidence of control implementation.
To streamline the documentation process, you can use compliance automation software specifically designed for ISO 27001. This software helps collect and organize evidence, saving you time and effort in preparing for the certification audit.
The certification audit is the final step in the ISO 27001 implementation process. It involves an external auditor reviewing your ISMS documentation, processes, and controls to ensure compliance with the standard’s requirements.
The audit typically consists of two stages: the Stage 1 audit and the Stage 2 audit. In the Stage 1 audit, the auditor assesses your documentation and confirms that the necessary policies and procedures are in place. The Stage 2 audit involves a more in-depth review of your processes and controls to ensure their effectiveness.
Upon successful completion of the certification audit, you will be issued an ISO 27001 certificate, valid for a specific period. The certificate demonstrates your organization’s commitment to information security and provides assurance to customers and stakeholders.
ISO 27001 is a continuous improvement process, and maintaining compliance requires ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and improvement of your ISMS. This involves conducting regular internal audits to identify areas of improvement, reviewing the effectiveness of controls, and addressing any non-conformities or gaps identified.
Continuous compliance also includes staying up-to-date with changes in the ISO 27001 standard and adapting your ISMS accordingly. It is essential to monitor emerging threats, technology advancements, and regulatory changes that may impact your information security practices.
By maintaining continuous compliance, you ensure that your ISMS remains effective in protecting your organization’s information assets and meeting the expectations of ISO 27001.
Implementing ISO 27001 is a comprehensive process that requires careful planning, coordination, and dedication. By following the phases outlined in this guide, you can establish a robust ISMS and achieve ISO 27001 certification.
Remember to assemble an implementation team, define the scope of your ISMS, perform a risk assessment and gap analysis, design and implement policies and controls, provide employee training, document your implementation efforts, complete a certification audit, and maintain continuous compliance.
ISO 27001 certification demonstrates your organization’s commitment to information security and can provide a competitive advantage in today’s digital landscape. So, take the necessary steps to protect your information assets and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your data
Copyright © 2025 Clear Infosec. All Rights Reserved.