- Email: info@clearinfosec.com
- 1800 760 5656

In our previous blog, we covered what Active Directory is and its functions. In this post, we will step foot into the world of Kerberos, a powerful network authentication protocol used in Active Directory. We’ll cover what Kerberos is, how it works, and its major components. Additionally, we’ll explain the need for Kerberos, highlighting why it is a crucial implementation for secure network authentication. Understanding Kerberos is essential for security professionals as many attacks abuse concepts related to this protocol. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of Kerberos and its role in Active Directory.
Kerberos is a centralized authentication protocol designed to provide strong security for client-server applications. Developed by MIT, it uses secret-key cryptography to authenticate users and services on a network, ensuring that data remains secure and confidential.
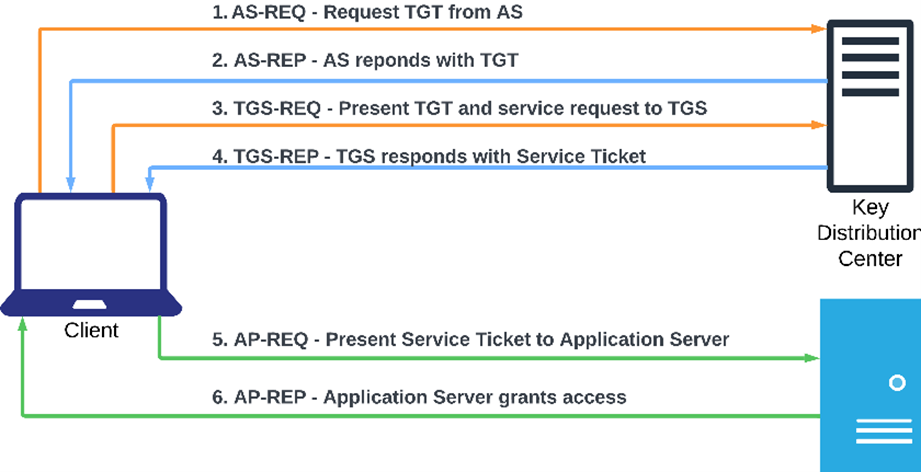
Kerberos authentication involves several key components that work together to ensure secure and reliable authentication:
The KDC is the core component of the Kerberos authentication protocol. It consists of two main services:
Validates the credentials of users and issues Ticket Granting Tickets (TGT).
Issues service tickets based on the TGT for access to specific network resources.
The user or application requesting access to a service.
The service that the client wants to access.
The responses from KDC and Service in Kerberos authentication contain several important elements:
6. Granting Access
7. PAC Validation
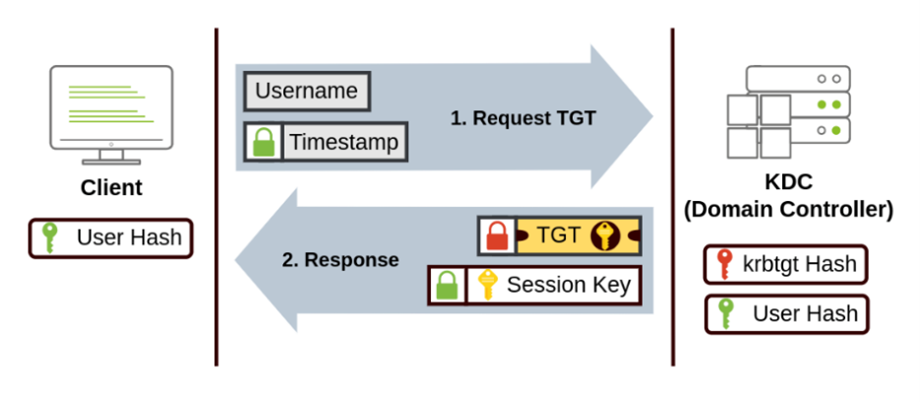
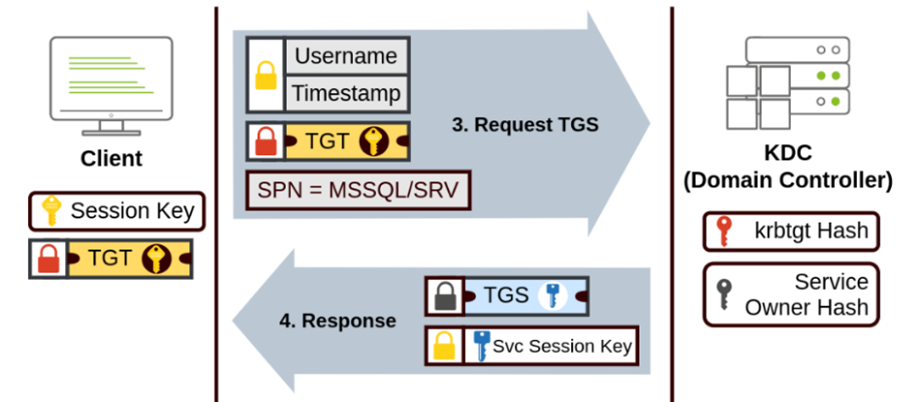
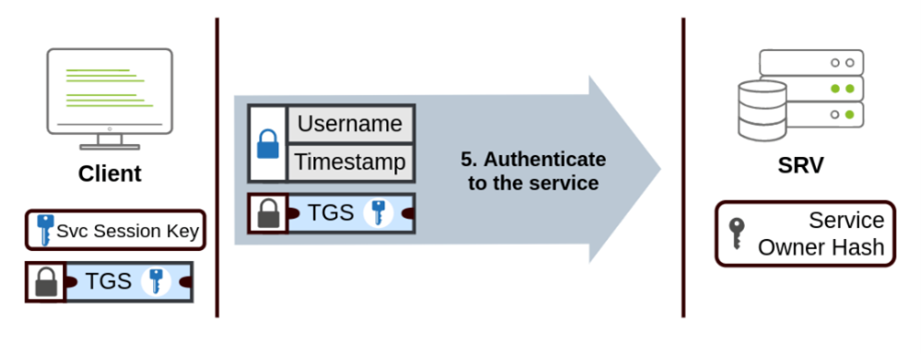
The Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) and the Ticket Granting Service (TGS) are crucial components of the Kerberos authentication process:
The TGT is issued by the AS after the user’s initial authentication. It serves as proof that the user has been authenticated and allows the user to request service tickets from the TGS without having to re-authenticate. This ticket simplifies the process and improves security by minimizing the number of times a user’s credentials are transmitted over the network.
The TGS is a part of the KDC that issues service tickets based on the TGT presented by the client. The TGS verifies the TGT and, if valid, provides a service ticket that the client can use to access the desired service.
The need for a ticket to get more tickets may sound a bit weird but this mechanism ensures that the user’s credentials are not repeatedly sent over the network and that each service access request is independently authenticated and authorized.
NTLM (NT LAN Manager)
NTLM is an older authentication protocol used in Windows environments. While NTLM is still supported for backward compatibility, it has several limitations:
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
LDAP is a protocol used to access and manage directory information. While it can be used for authentication, it primarily focuses on querying and modifying directory services. LDAP alone is not sufficient for comprehensive authentication due to the following reasons:
With a solid understanding of Kerberos and its authentication mechanisms from this post, combined with the foundational knowledge of Active Directory from our previous blog post, you are now well-prepared to learn further about widely used Active Directory attack techniques. In our next series of posts, we will guide you through some of the common issues faced when joining a Kali machine to Active Directory and explore different attacks on Active Directory. Stay tuned!
Copyright © 2026 Clear Infosec. All Rights Reserved.